Direct Hydrocarbon Indicator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In reflection seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflection (physics), reflected seismic waves. The method requir ...
, a hydrocarbon indicator (HCI) or direct hydrocarbon indicator (DHI) is an anomalous seismic attribute
In reflection seismology, a seismic attribute is a quantity extracted or derived from seismic data that can be analysed in order to enhance information that might be more subtle in a traditional seismic image, leading to a better geological or geo ...
value or pattern that could be explained by the presence of hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may b ...
in an oil or gas reservoir.
DHIs are particularly useful in hydrocarbon exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for hydrocarbon deposits, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.
Exploration methods
...
for reducing the geological risk of exploration wells. Broadly, geophysicists recognize several types of DHI:
* Bright spot
In reflection seismology, a bright spot is a local high amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon explor ...
s: localized amplitudes of greater magnitude than background amplitude values. Equipment prior to the 1970s had the bright spots obscured due to the automatic gain control
Automatic gain control (AGC) is a closed-loop feedback regulating circuit in an amplifier or chain of amplifiers, the purpose of which is to maintain a suitable signal amplitude at its output, despite variation of the signal amplitude at the inpu ...
.
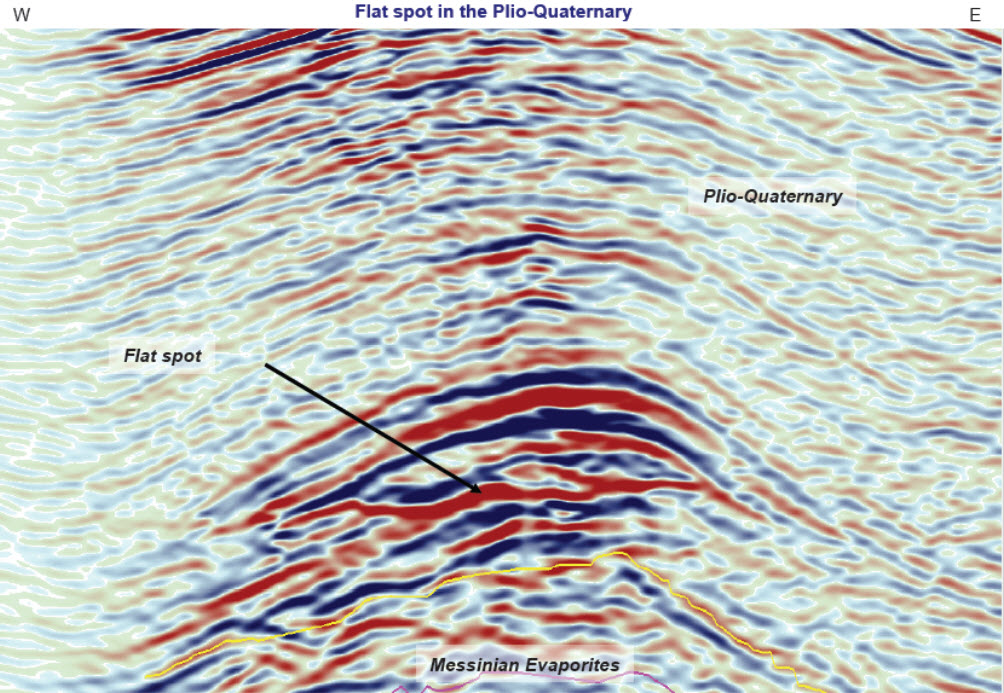
* Flat spots: nearly horizontal reflectors that cross existing stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
, possibly indicating a hydrocarbon fluid level within an oil or gas reservoir.
* Dim spots: low amplitude anomalies.
* Polarity reversals can occur where the capping rock has a slightly lower seismic velocity than the reservoir and the reflection has its sign reversed.
Some geoscientists regard amplitude versus offset
In geophysics and reflection seismology, amplitude versus offset (AVO) or amplitude variation with offset is the general term for referring to the dependency of the seismic attribute, amplitude, with the distance between the source and receiver ( ...
anomalies as a type of direct hydrocarbon indicator. For example, the amplitude of a reflection might increase with the angle of incidence, a possible indicator of natural gas.
References
{{petroleum-stub Geophysical imaging Petroleum geology